1. What is sickle cell anaemia? |
2. Symptoms of the disease |
3. Bone marrow transplantation |
4. Blood transfusion |
5. Medical therapy |
6. Gene therapy |
7. Clinics for treatment |
Sickle cell anaemia (SCA) is an inherited disease which makes red blood cells irregularly shaped due to a genetic mutation and causes them to prevent normal blood flow. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute estimates that about 20 million people worldwide suffer from the disease. Serious health risks of SCA include bouts of pain due to blocked blood vessels, anaemia, infections, strokes and organ damage. Doctors around the world are striving not only to alleviate the symptoms of this disease but also to prevent its complications. The main method of therapy is bone marrow transplantation. Gene therapy, which has only recently been discovered, is beginning to play a major role in the treatment of sickle cell anaemia. The efforts of the medical community in research, development of new technologies and more effective treatment methods are actively moving forward to alleviate the course of this disease. Read more to learn about this disease and its treatment.
What is sickle cell anaemia?
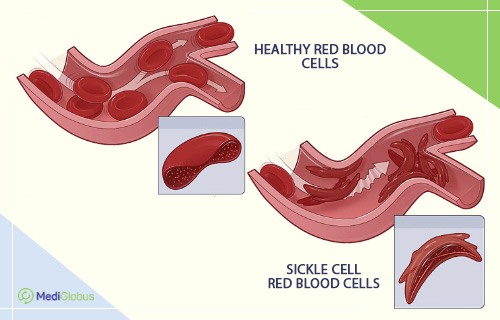
Sickle cell anaemia is a group of blood disorders associated with damage to red blood cells. Red blood cells contain the protein haemoglobin, whose main function is to carry oxygen from the lungs to other tissues and organs.
The shape of red blood cells is usually round and flexible, which allows them to pass easily through narrow capillaries and maintain normal blood flow. In the case of SCA, red blood cells take on an abnormal shape. As a result of these changes, they die prematurely, leading to a permanent deficiency of red blood cells (anaemia). In addition, these abnormal cells cannot move freely through small blood vessels; they tend to get stuck, obstructing the free flow of blood. Vascular blockage causes pain and a variety of serious complications including infections, acute bronchospasm and strokes.
There are several types of SCA, each determined by genes inherited from parents:
HbSS | Humans inherit two genes from their parents that are associated with “S” haemoglobin. As a consequence, the red blood cells take on a sickle-like shape and become rigid. This is the most severe form of the disease. |
HbSC | People with this form of the disease inherit the “S” gene from one parent and the “C” gene from the other parent. This type of pathology is considered less dangerous. |
HbS beta-thalassaemia | In this case, a person inherits the “S” gene from one parent and the beta-thalassaemia gene from the other parent. This type of disease can be either severe or mild. |
HbSD, HbSE, and HbSO | These are rare forms of sickle cell anaemia. In this case, a person inherits the “S” gene from one parent and various other abnormal genes (“D”, “E”, “O”) from the other. |
HbAS | A person acquires the abnormal “S” gene from one parent and the normal “A” gene from the other parent. In such a case, symptoms of the disease may be absent or may only appear with significant physical exertion or dehydration. A person with HbAS is not considered to have the disease but may pass the abnormal “S” haemoglobin gene to their children. |
Symptoms of sickle cell anaemia
Sickle cell anaemia is a condition that a person is born with. Most newborns do not experience problems until they are about 5 or 6 months old. Symptoms can vary from person to person and change over time.
Early symptoms include:
jaundice – yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, which occurs when large numbers of destroyed red blood cells accumulate;
severe fatigue or irritability as a consequence of anaemia;
swelling of the hands and feet.
Dangerous symptoms that may indicate a serious health risk include:
severe anaemia that is manifested by extreme weakness, difficulty breathing, dizziness, and heart rhythm disturbances;
body temperature above 38,5 degrees Celsius. It requires attention from a specialist and antibiotic treatment immediately, and in some cases – hospitalisation;
bronchial spasm, which is accompanied by chest pain, cough, fever and shortness of breath (may require hospitalisation, antibiotics, oxygen therapy or blood transfusion);
sudden weakness, numbness on one side of the body, slurred speech, and trouble seeing or walking that may be symptoms of a stroke and require immediate medical attention;
priapism – an erection that lasts 4 hours or more (this condition requires urgent medical attention).
Book a free consultation to find out how to go for treatment at one of the certified clinics abroad.
Diagnostic methods for sickle cell anaemia
If sickle cell anaemia is suspected, it is necessary to undergo an examination, which includes the following diagnostic methods:
Blood test | Blood tests detect the presence of abnormal haemoglobin. |
Genetic tests | Help determine the type of sickle cell anaemia and confirm the diagnosis if blood results are inconclusive. They also determine if a person carries one or two abnormal haemoglobin genes. |
Prenatal screening | Medical professionals can make a diagnosis even before the baby is born. This is done by analysing samples of amniotic fluid or tissue taken from the placenta. This type of testing can be done from 8-10 weeks of pregnancy. |
Newborn screening | Blood is taken from a newborn baby’s heel and examined for abnormal haemoglobin. |
Treatment of sickle cell anaemia
For some patients, bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is the only therapy for sickle cell anaemia. The disease can also be treated with drug therapy to prevent and control any complications (chronic pain, anaemia, risks of severe infections, etc.). In addition, there is now active research and development of gene therapy methods that can not only prevent the development of dangerous complications but also completely get rid of this disease.
Bone marrow transplantation
Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is currently the primary FDA-approved treatment for sickle cell anaemia. The goal of the procedure is to replace abnormal cells with healthy stem cells from a donor. However, this treatment is not suitable for every person as it is quite difficult to find a suitable donor. BMT is mainly performed on children who have a high risk of developing severe complications. The procedure is not often prescribed for adults, as the older the patient is, the harder he/she endures treatment and recovery. About 85% of transplants in children are successful. However, the probability of complications is still high. The most common complications after transplantation are seizures, infections and other consequences. Autoimmune reactions (“graft versus host”) are the most dangerous complication, when donor cells start attacking other cells of the patient, causing damage to internal organs and systems.
The BMT procedure consists of several stages:
Preparatory stage | Before transplantation, the patient undergoes chemotherapy and total radiation therapy to destroy the bone marrow. |
Stem cell transplantation | The patient is then injected with healthy bone marrow stem cells from a compatible donor through a vein. |
Potential donors | Ideal bone marrow donors are siblings. |
Methods of collecting stem cells from a donor | There are 2 ways of collecting bone marrow cells from a donor – peripheral and collection through the pelvic bone. In the peripheral collection, the donor is given a medicine that stimulates the growth of stem cells in the blood. The blood is then drawn from the vein and processed to isolate the stem cells. If the donor’s veins are too narrow, the stem cells can be harvested through the pelvic bone under general anaesthesia. The procedure is safe and the patient usually goes home the same day. |
After transplantation | After the new stem cells are injected, the patient needs a few weeks before the new cells begin to grow. During this time, the immune system is at its weakest. Therefore, the patient is placed in a special room to isolate them and protect them from infections. |
Effectiveness of BMT in sickle cell anaemia
Bone marrow transplantation is highly effective in the treatment of sickle cell anaemia, especially in children. According to the studies of the Paediatric Working Group of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, the 5-year overall survival rate after BMT is 95% for children under 16 years of age and 81% for those aged 16 years and older. Separately, the 5-year survival rates without graft-versus-host disease, which is a complication after BMT, in these age groups were 86% and 77%, respectively.
To go for a bone marrow transplant abroad, leave an application on the website. A MediGlobus specialist will help you choose a clinic, make an appointment without a waiting list and help you organise your trip.
Blood transfusion
Blood transfusion for patients with sickle cell anaemia is necessary when severe anaemia develops, acute chest syndromes, stroke, or multiple organ failure, before surgery to prevent complications and during pregnancy. Regular blood transfusions are also used to prevent primary and secondary strokes in children, and if medication is not effective in controlling pain. Blood transfusions help to reduce the number of emergency room visits, hospitalisations and days in hospital due to pain crises and other complications.
Drug therapy
Various medications are used in the treatment of sickle cell anaemia:
Voxelotor is recommended for adults and children from 4 years of age. It prevents red blood cells from forming a “sickle” shape and sticking together. The drug helps to reduce the destruction of red cells, reduces the risk of anaemia and improves blood flow to organs. Possible side effects include headache, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, nausea, fatigue and fever.
Crizanlizumab-tmca is approved for adults and children 16 years of age and older. It prevents red blood cells from sticking to the walls of blood vessels, which helps avoid blocked blood flow, inflammation, and painful crises. Possible side effects include nausea, joint pain, back pain and fever.
Hydroxyurea is indicated to reduce or prevent several complications of SCA. It is used in both adults and children. It can reduce the number of painful attacks as well as improve blood quality and reduce the need for transfusions and hospitalisations. Possible side effects include decreased white blood cell or platelet counts. These side effects usually disappear when the patient stops taking the drug.
L-glutamine is a drug approved by the FDA for patients 5 years of age and older to reduce the level and frequency of pain attacks. Studies have shown that patients who take L-glutamine have fewer hospitalisations. The drug is taken as a powder that is added to liquids or food. Possible side effects include nausea, fatigue, chest and muscle pain.
Penicillin is prescribed to reduce the risk of serious infections. The drug can be used for both children and adults.
These medications represent only a part of the therapy course for sickle cell anaemia and their use is determined by the doctor depending on the individual needs and characteristics of the patient. With SCA, patients may experience various complications, such as priapism, bone or joint pain, delayed sexual development in children, formation of leg ulcers and others. In such a case, depending on the particular problem, the doctor prescribes a set of necessary medications.
Gene therapy for sickle cell anaemia
Gene therapy is a new treatment for SCA that received FDA approval in December 2023 for patients 12 years of age and older. This therapy includes two new drugs: exagamglogene autotemcel (Casgevy) and lovotibeglogene autotemcel (Lyfgenia).
Casgevy alters blood cells so that they begin to produce normal haemoglobin A. Studies have reported that 95-100% of patients who received this therapy did not experience a vaso-occlusive crisis for 12 to 18 consecutive months and did not require hospitalisation.
Lyfgenia introduces healthy genes and corrects mutations associated with SCA. Studies have shown that this therapy results in a lasting reduction in disease manifestations in patients after a single course. Patients did not experience severe symptoms or require hospitalisation for 18 months after therapy.

Which clinics treat sickle cell anaemia?
The treatment of sickle cell anaemia requires a serious approach, as the disease is associated with many life-threatening complications. Abroad, therapy is carried out in specialised haematology departments, which have all the necessary resources for this purpose. Treatment is carried out by haematologists with many years of experience, who know all effective methods of therapy for this disease, including BMT.
Turkey
Spain
Israel
Germany
Summary
Sickle anaemia is an inherited blood disorder. It is caused by a mutation in the gene responsible for the synthesis of haemoglobin, which leads to changes in the structure of red cells, their premature destruction and their tendency to clump in blood vessels.
Among the main manifestations of the disease are attacks of pain, anaemia, impaired circulation, development of stroke and deterioration of the general condition of the body.
To find out whether a person has sickle cell anaemia, a blood test is carried out. The study allows the detection of unusual forms of haemoglobin.
Treatment for sickle cell anaemia includes medical therapy, blood transfusions, bone marrow transplantation and other methods to manage pain and reduce the risk of complications. As of December 2023, the FDA has approved 2 gene therapies.
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure in which healthy bone marrow stem cells from a donor are transplanted into a patient to replace unhealthy cells. This method helps in the treatment of sickle cell anaemia, especially in children with severe forms of the disease. However, BMT can be associated with certain risks, including graft-versus-host disease and other complications.
Blood transfusion for sickle cell anaemia is used for severe anaemia and chronic pain, and to prevent stroke and before surgery.
Drug therapy for sickle cell anaemia includes the use of drugs such as hydroxyurea, voxelotor and others aimed at preventing pain crises, reducing red blood cell destruction and reducing complications associated with the disease.
Gene therapy has emerged as a promising area of treatment for sickle cell anaemia. In December 2023, the first two gene-editing drugs were approved for severe SCA in patients over 12 years of age. The drugs are exagamglogen autotemcel (Casgevy) and lovotibeglogen autotemcel (Lyfgenia). They can prevent the development of crises and reduce the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Modern methods of SCA therapy are available in leading clinics in Turkey, Spain, Israel and Germany.
You can get all the information you need about sickle cell therapy from the medical experts at MediGlobus. Click on the button below and leave a contact to get in touch. A coordinator will call you back as soon as possible and answer all your questions. MediGlobus will also help you to organise your travel for treatment as soon as possible.
Sources:
- 1. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
- 2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- 3. Sickle cell disease – NHS
- 4. Medscape
- 5. American Society of Hematology
- 6. National Library of Medicine
















