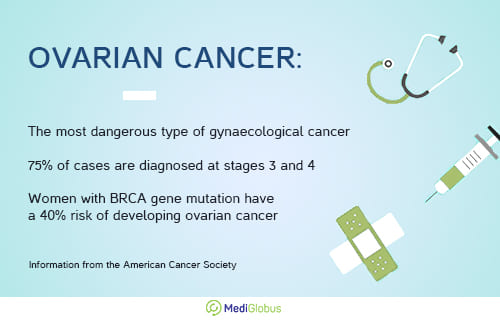
Ovarian cancer is one of the most common types of cancer among women. The difficulty in treating this disease is that 75% of cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage. In contrast to advanced cases, early-stage ovarian cancer can be cured in 95% of cases.
Treatment for ovarian cancer is most effective when it is tailored to the individual patient’s needs, maximising the effectiveness of therapy and prolonging their life. The main methods of cancer therapy are surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and hormonal therapy. In recent years, more advanced therapies such as targeted therapy and HIPEC chemotherapy have emerged.
Read more about how ovarian cancer is treated depending on the stage in our article.
Listen to the article:
Types and symptoms of ovarian cancer
In 87.8% of cases, ovarian neoplasms are benign. This means that they do not require aggressive chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The remaining 12.2% of cases are ovarian cancer. It is divided into types:
Epithelial tumours of the ovary account for 85-90% of all cases of cancer of the organ. They are divided into two types: slow-growing and fast-growing. The latter respond better to chemotherapy.
Primary peritoneal carcinoma – similar to epithelial tumours but originating from the tissue of the fallopian tubes.
Embryonal cell tumour of the ovary (germinoma) – forms from oocytes and has a good prognosis for treatment.
Ovarian stromal tumours – usually occur in women over 50 years of age. Because the disease manifests itself in its early stages through vaginal bleeding, it is often detected in time and removed completely.
Depending on the type of ovarian cancer, the symptoms and treatment may differ. In many cases, the disease does not manifest itself in its early stages, causing women to miss it. To prevent this, it is advisable to have regular female check-ups, especially for those with a family history of cancer.
The most common symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
Swelling;
Lower abdominal pain;
Low appetite;
Frequent urination or the constant feeling of a full bladder;
Disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Sign up for a women’s check-up
MediGlobus specialists will help you find a check-up package at one of the leading foreign clinics. Contact our coordinating physicians for a free consultation by clicking on the button below and leaving your contact details.
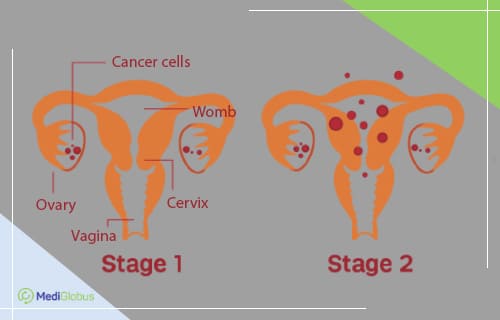
Treatment of stage 1 ovarian cancer
In stage 1, the cancer is limited to one ovary and the fallopian tube (stage 1A) or both ovaries and fallopian tubes (stage 1B). There is also stage 1C – a tumour with a damaged capsule, which indicates the risk of cancer spreading through the body.
The main treatment for ovarian cancer is the surgical removal of the tumour. A hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy is usually performed for this purpose. During this surgery, the doctor completely removes the uterus, fallopian tubes, both ovaries and the fatty tissue surrounding these organs. Also during the procedure, the surgeon biopsies local lymph nodes and takes a sample of fluid if it is present in the abdominal cavity. This is done to send the tissue for laboratory analysis and correctly determine the stage of the disease.
The procedure takes one to three hours and leaves a small scar on the lower part of the pelvis. In modern clinics, it is performed using the da Vinci robot, which avoids much blood loss, shortens the rehabilitation period and leaves smaller scars.
With unilateral stage 1A ovarian cancer, it is possible to remove only the affected part of the organ and retain fertility.
For fast-growing stage 1 ovarian cancer, 3-6 cycles of chemotherapy are given after surgery. The choice of drugs depends on the type of tumour and how aggressive it is.
Patients with ovarian cancer can preserve the possibility of motherhood by freezing eggs or embryos. They can later have a healthy baby by resorting to IVF with a surrogate mother.
Treatment of stage 2 ovarian cancer
In stage 2, testicular cancer spreads to the uterus, bladder, rectum or sigmoid colon.
Cytoreductive surgery is used to treat stage 2 ovarian cancer. In addition to the reproductive organs, the surgeon removes all neoplasms found in the abdomen. This procedure aims to leave no visible cancer larger than 1 cm. Patients who have undergone this procedure successfully have a better prognosis than those who are left with larger tumours. Smaller neoplasms respond well to adjuvant chemotherapy, so they are usually not very threatening.
Laparoscopic cytoreductive procedures are available in specialised cancer centres. This surgery is different in that the surgeon does not make large incisions in the abdomen, but instead operates with special instruments inserted through small openings. The advantages of laparoscopic surgery for ovarian cancer are that there is no abdominal decompression procedure. In addition, patients have less blood loss, less scarring, experience less pain and are discharged from the hospital sooner. However, laparoscopic surgery may not be indicated for all women with ovarian cancer. The doctor’s recommendations depend on the specifics of the individual case and the balancing of the benefits and risks of minimally invasive surgery.
At least 6 courses of chemotherapy are given after surgery for stage 2 ovarian cancer. In some patients, intraperitoneal treatment may be recommended instead of intravenous treatment.
Hormone therapy is also used to treat stages 2-4 ovarian stromal tumours. It reduces the level of oestrogen in the body, which in turn slows down the growth of the tumour. This type of cancer has a high risk of recurrence, so women remain under close observation by an oncologist for the next few years.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT FOR A CONSULTATION WITH AN ONCOLOGIST
Ovarian cancer in its early stages is often mistaken for other diseases. An experienced oncologist will be able to prescribe the right diagnosis and treatment. For a consultation with an international specialist with over 20 years of experience in treating ovarian cancer, visit the MediGlobus website by clicking the button below.
Treatment for stage 3 ovarian cancer
In stage 3 ovarian cancer, the disease has spread to the lymph nodes and nearby pelvic organs, including the bowel, spleen and liver.
The mainstay of treatment for stage 3 ovarian cancer, as well as stage 2, is cytoreductive surgery. This involves removing the tumour along with the surrounding tissue. Patients may have to have part of their intestine, bladder or liver resected, depending on the location of the tumour. Any lymph nodes where malignant cells have been detected and the fatty tissue lining the inner walls of the pelvis will also be removed.
After the patient has recovered from the operation, combined chemotherapy is prescribed. The treatment is carried out with a combination of drugs that reinforce each other’s anti-tumour effects. Specific chemotherapy protocols are chosen based on many factors: the specific type of cancer, degree of malignancy of the tumour, age and condition of the patient, response to previous treatments, etc. The therapy can be administered intravenously or intraperitoneally. The latter option is used if cytoreductive surgery has been successful and the surgeon has been able to remove all large tumours completely.
Targeted therapy is also available for stage 3 ovarian cancer. The FDA has approved six drugs to treat this type of cancer. Targeted drugs differ from traditional chemotherapy in that they aim at specific areas of cancer cells. This means that they cause fewer side effects. But also because of this, targeted therapy is not suitable for everyone. Before treatment, doctors carry out genetic tests on cancer cells to make sure that they have the mutations needed for the drug to work properly. A course of targeted therapy for ovarian cancer usually lasts about a year.
Treatment for stage 3 ovarian cancer is accompanied by careful monitoring of the patient’s condition. Doctors monitor the progression of the tumours with CT scans, MRI scans, PET-CT scans, and measurements of the CA-125 oncomarker in the blood.
Patients for whom surgery is contraindicated for health reasons are given three cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. If the treatment works, the tumours will shrink and surgery will be possible.
Supportive therapy may also be recommended for some women. It is prescribed after chemotherapy with platinum drugs (cisplatin or carboplatin) if cancer has shrunk a lot or disappeared completely. The treatment aims at destroying the cancer cells that remain after the main course of chemo but are too small to be seen in the tests. Maintenance therapy aims to prevent a relapse.
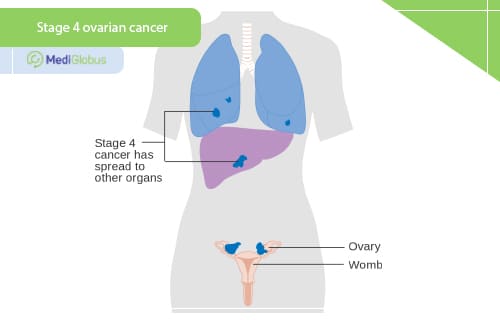
Treatment for stage 4 ovarian cancer
In stage 4 ovarian cancer, the disease forms metastases in the liver, lungs, bones and other distant organs. These are difficult to treat. Often the treatment plan is to keep the patient alive and well. Pleural effusion – an accumulation of fluid in the tissue surrounding the lungs – can often occur during this disease.
Treatment for ovarian cancer at stage 4 is similar to that for stage 3. Oncologists carry out cytoreductive surgery in combination with adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, as well as targeted therapy.
Radiotherapy is used to treat distant metastases of stage 4 ovarian cancer, especially those located in the brain and spinal cord. The treatment course usually lasts several weeks.
In cases where the prognosis is poor, the oncologist may offer palliative treatment. The aim is not to cure the disease, but to improve the patient’s condition. Treatment provided by a team of specialists helps to control the pain and symptoms of the disease and the side effects of medication. Cancer patients may need surgery to remove fluid accumulation in the abdomen or bowel obstruction.
Since 2018, leading scientific institutes have been investigating the effectiveness of HIPEC therapy in the treatment of stage 4 ovarian cancer. The procedure involves injecting chemotherapy heated to 42° C into the abdomen. This method has already been approved for the treatment of end-stage colon and pancreatic cancers. The survival rate of patients after HIPEC chemotherapy increases by 7%. However, it is a complex and dangerous procedure that is only available in the most experienced specialist cancer centres.
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT BOOKING
To book an appointment for ovarian cancer treatment at a foreign clinic, leave an application on the MediGlobus website. We will help you choose a clinic based on your budget, get you an invitation to treatment within a week and fully organise your trip.
The prognosis for survival in ovarian cancer
The five-year survival rate is a measure of what percentage of patients with this stage of ovarian cancer who live more than 5 years. If there is no recurrence during this period, the risk of the disease coming back becomes very low.
It should be remembered that survival statistics are average and do not guarantee an outcome in each case. For a more accurate prognosis, you should always consult your oncologist, who will be able to provide patient- and disease-specific information.
| Stage | 5-year survival rate |
|---|---|
| Stage 1A ovarian cancer | 94% |
| Stage 1B ovarian cancer | 92% |
| Stage 1C ovarian cancer | 85% |
| Stage 2A ovarian cancer | 78% |
| Stage 2B ovarian cancer | 73% |
| Stage | 5-year survival rate |
|---|---|
| Stage 2C ovarian cancer | 57% |
| Stage 3A ovarian cancer | 59% |
| Stage 3B ovarian cancer | 52% |
| Stage 3C ovarian cancer | 39% |
| Stage 4 ovarian cancer | 17% |
Clinics for the treatment of ovarian cancer
The story of the patient who beat ovarian cancer

Doris was diagnosed with ovarian cancer in 2019 when she was 70 years old. She went to her GP with symptoms not suggestive of gynaecological problems: bloating, abdominal pain and diarrhoea. At first, she was diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome – ovarian cancer is often mistaken for this illness.
After six months of unsuccessful treatment, Doris was admitted to the hospital with severe abdominal pain. In the emergency department, the woman was referred for an MRI and CT scan, which revealed stage 4B ovarian cancer. At this point, cancer has formed multiple metastases, which had been causing the pain all along.
According to the standard treatment plans for this disease, the woman first underwent three courses of combined chemotherapy. This was followed by cytoreductive surgery. The surgeon completely removed her uterus and ovaries, as well as some pelvic tissue, her spleen and a large tumour on her diaphragm. Doris then underwent three more courses of chemotherapy as well as long-term hormone therapy.
At this stage of the disease, doctors use aggressive oncotherapy to maximise the chances of the cancer being eradicated. This treatment is difficult for those affected, but thanks to the support of her husband, her active lifestyle and her positive attitude, Doris has been able to endure all the hardships.
Despite unfavourable statistics, Doris has achieved a recurrence of stage four ovarian cancer. She advises all women who have faced the same ordeal as she has, not to give up.
Summary
Ovarian cancer is the fifth most common cancer among women. It is well treated in its early stages, but in most cases, it is diagnosed at a late stage. The tumour can remain undetected for a long time, and often the symptoms of ovarian cancer are mistaken for gastroenterological diseases or benign cysts.
In stage 1 ovarian cancer, the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed. If possible, patients of childbearing age may be left with one ovary to preserve fertility. Chemotherapy is carried out after the operation.
In stage 2 ovarian cancer, cytoreductive surgery is performed. During this, all the tumours detected are removed in addition to the internal genitalia. A long course of combined chemotherapy is also used.
Treatment for stage 3-4 ovarian cancer consists of a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, radiation and targeted therapy. The doctor aims to remove all the cancer cells in the body and achieve a stable remission, or to improve the patient’s well-being.
In stage 1, 90% of patients with ovarian cancer live more than 5 years. In stage 2, this falls to 70%, in stage 3 to 39% and in stage 4 to 17%.
Our patients most often seek treatment for ovarian cancer in hospitals in Turkey, Germany, Spain and the Czech Republic. Quality therapy, including laparoscopic and robotic surgery, is available at the Medicana, Liv, Anadolu, Motol, Uniclinica Navarra and the University Hospital of Cologne.
OVARIAN CANCER TREATMENT BOOKING
MediGlobus coordinating doctors will help you with selecting a clinic, collecting documents for treatment abroad, translating statements, opening a visa, booking flights and accommodation, finding an interpreter and solving any other problems during your stay abroad. All consultation services of our specialists are free of charge.
Sources:
- 1. Ovarian cancer survival statistics from the American Association of Oncologists.
- 2. Cancer Research UK on the treatment of stage IV ovarian cancer.
- 3. Oncology Letters: Effective treatment of a patient with stage IV ovarian cancer
- 4. The New England Journal of Medicine: Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer











