1. Symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma |
2. Merkel cell tumour diagnosis |
3. Treatment for Merkel cell cancer |
4. Patient prognosis |
5. Recommended hospitals |
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare, aggressive form of skin cancer. The disease occurs in only 3 people per million. In 97% of cases, patients are over 50 years old. Men are twice as vulnerable as women.
The danger of Merkel cell tumour is that it can be mistaken for other dermatological or oncological diseases. This can result in missing the window for early treatment, which is short-lived due to the highly aggressive nature of the disease. Therefore, Merkel cell carcinoma is considered to be 5 times more dangerous than melanoma.
Read more in this article about the care options available at leading foreign hospitals for the diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma.
What is Merkel cell carcinoma and what are its symptoms?
Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine skin tumour – a type of skin cancer. It is a very rare disease, which can make it difficult for less experienced doctors to correctly diagnose and select the right treatment.
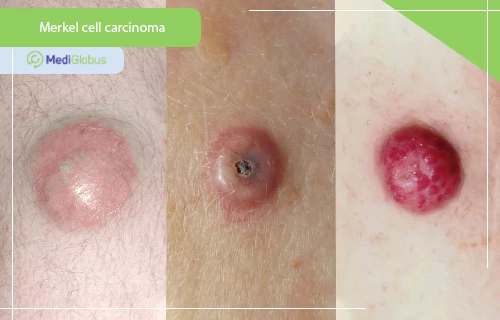
Merkel cell tumour differs in appearance from melanomas. It usually appears as a small subcutaneous nodule – most often reddish or bluish, but in some cases, it remains colourless. Patients may mistake it for an insect bite or a large cyst. The most characteristic symptom of the disease is the rapid growth of the tumour – developing over several months or even weeks. The average size of the tumour is 2 cm in diameter.
The tumour in Merkel cell carcinoma is painless; however, it can be sensitive to touch and cause itching. The most common locations are the skin areas that are most exposed to the sun – the face (especially the eyelids), head, neck; sometimes the exposed areas of the arms and legs.
Merkel cell carcinoma is called this way because the cancerous cells look like Merkel cells under the microscope. These are part of the epidermis of the skin whose function is linked to the nerve endings responsible for the sensation of touch.
Because Merkel tumour is a rare and aggressive cancer, its untimely detection is a particular problem. In addition, about half of the patients are misdiagnosed when they first go to the doctor. As the disease progresses, treatment becomes increasingly difficult and the risk of recurrence increases.
Make an appointment
An online or face-to-face consultation with a dermatological oncologist is the first step towards a correct diagnosis. If you already have your laboratory results, you can send them to your doctor to receive an accurate diagnosis from home.
Diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma
Diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma involves a dermatological examination as well as laboratory and imaging tests.
The main methods doctors use when diagnosing skin cancer include:
A skin biopsy is a procedure in which the doctor takes a small sample of tissue from a tumour for laboratory diagnosis. There are two options for this procedure – punch biopsy (carried out using a special pen-like instrument) and slice biopsy (cutting off a thin layer of the tumour with a scalpel). The choice of the best method of diagnosis is left to the doctor, depending on the specific clinical case. A skin biopsy can not only show whether a tumour is cancerous but also in some cases whether or not cancer has managed to penetrate the lymphatic pathways.
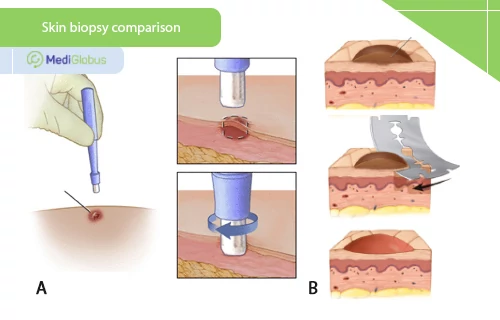
Signal lymph node biopsy is a procedure that is carried out to determine the extent to which cancer has spread. To start with, the doctor injects the patient with a small amount of contrast agent near the tumour. This will reveal which lymph nodes (there may be one or more) are closest to the neoplasm. These will have to be removed and examined by the laboratory. The presence of cancer cells in them indicates that the cancer is highly likely to have spread throughout the body, which will require a more aggressive and systematic approach to treatment.
Immunohistochemistry is a laboratory test that uses antibodies to check for the presence of certain markers in a patient’s tissue sample. In the case of Merkel cell carcinoma, doctors look for the MCPyV antibodies. The results of this test will be useful in making a prognosis for the disease as well as monitoring the progress of treatment. It is also used during cancer check-ups after treatment has ended to check for recurrence.
Because of its highly aggressive nature, Merkel cell carcinoma often forms metastases in the lungs, liver, bones or brain. Because of this, imaging tests are a must for patients with this diagnosis. Doctors may prescribe:
Computed tomography (CT) scan
This method uses X-rays to create detailed images of the chest and abdomen from different angles. Often a contrast agent is injected into the patient before the procedure begins. This has the property of illuminating malignant tumours in the images taken. This substance is safe for the patient, and after a few hours, it is eliminated from the body.
Positron emission tomography (PET)
This is a method of computerised examination of your internal organs. It involves injecting a small amount of radiation glucose into the patient intravenously, which works in a similar way to contrast in a CT scan. Cancer cells will look brighter on the scan because they take in more glucose than healthy cells.
Merkel cell carcinoma is a very rare disease. However, people with risk factors should take heed of their well-being and see a doctor immediately if any suspicious growths are detected. Particular attention should be paid to:
People who are exposed to a lot of ultraviolet light. This applies to those who spend a lot of time outdoors, residents of sunny countries and sunbed users.
Patients who have been previously diagnosed with other types of skin cancer.
In patients with a weakened immune system – due to diseases (HIV, chronic leukaemia); taking medications that weaken the immune system; or having undergone BMT.
Elderly people and people with pale skin.
Stages of Merkel carcinoma
Stage 0 (carcinoma in situ) | An ‘in situ’ tumour is considered a precancerous condition. With a skin biopsy, the doctor will find abnormal Merkel cells in the upper layers of the skin that only have the potential to become cancerous. |
Stage 1 | Tumour up to 2 cm in diameter. |
Stage 2 | Stage 2 Merkel cell carcinoma is divided into two substages: 2A and 2B. Group 2A includes all tumours larger than 2 centimetres and group 2B includes tumours that have started to spread to neighbouring tissues (skin, muscle, cartilage, bone, etc.) |
Stage 3 | Stage 3 is also divided into subgroups. Merkel’s 3A tumour is characterised by all the criteria mentioned in the previous stages as well as positive results from a biopsy of the signal lymph node. Merkel’s carcinoma in stage 3A is also diagnosed if the first symptom detected by the physician is an enlarged lymph node, the biopsy of which will confirm the presence of the cancer process.
Stage 3B is diagnosed when:
|
Stage 4 | In stage 4, Merkel carcinoma forms distant metastases in the bones, liver, lungs or brain. |
Find a skin cancer clinic
Please contact the MediGlobus medical coordinators for assistance, and we will advise you free of charge on cancer treatment abroad, as well as help you with choosing a clinic and making travel arrangements.
Treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma by stage
Treatment of Merkel cell tumour at stages 1 and 2
Treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma depends on the stage at which the disease was detected. In stages 1 and 2, doctors carry out surgical removal of the tumour, supplemented by radiation therapy.
Surgeries carried out to treat Merkel cell carcinoma:
Wide local excision is the standard procedure for treating skin cancer. The surgeon removes the tumour along with a small amount of tissue surrounding it. This is done to make sure that no cancer cells are left in the body that could cause a recurrence.
Mohs surgery is a modified procedure that is used to treat skin tumours. Instead of removing the entire tumour at once, the tumour is sectioned layer by layer. Each time the removed tissue is examined under a microscope in the operating theatre for the presence of cancer cells. Mohs surgery usually leads to better treatment results – both in terms of scarring and in terms of obtaining a clean resection edge.
A lymph node dissection is a surgical procedure in which lymph nodes are removed and a tissue sample is examined under a microscope for signs of cancer.
After the surgery, doctors typically use radiotherapy to destroy the remaining cancer cells. It can also be used as the only treatment for people who choose not to have surgery.
Treatment of a Merkel cell tumour at stage 3
For stage 3 tumours, surgery and radiotherapy remain the main treatment methods. Immunotherapy can be used in addition to these. It shows good results in treating the metastatic spread of cancer. In rare cases, doctors may suggest chemotherapy.
Immunotherapies are drugs that can “activate” the patient’s immune system to fight cancer on its own, “training” it to distinguish cancer cells from healthy ones and destroy them. A type of immunotherapy called “immune checkpoint inhibitors” is used to treat Merkel cell carcinoma. There are several drugs of this type that are approved to treat aggressive skin cancer. Studies show that 50-65% of patients with this diagnosis have a positive response to immunotherapy.
Treatment of a Merkel cell tumour at stage 4
The main treatment for stage 4 Merkel cell cancer is immunotherapy. In addition, doctors may prescribe surgery, radiation therapy or chemotherapy as palliative care. The patient’s treatment plan is individualised, depending on the location of the metastases and the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment of a recurrent Merkel cell tumour
Merkel cell tumours recur relatively frequently. In this course of events, doctors use the same set of techniques as in standard protocols; however, the approach may be more aggressive to increase effectiveness. The surgeon may remove an additional area of skin at the site of the initial surgery, and may also excise several more lymph nodes. Radiotherapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are also actively used during the treatment of relapse.
The prognosis for the treatment of Merkel carcinoma
According to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC), “the prognosis of patients with Merkel carcinoma varies significantly, particularly depending on the stage of the disease”. Other factors affecting a patient’s prognosis include:
Histological characteristics of the tumour;
Presence or absence of viral MCV infection;
Immune status of the patient.
These factors should be kept in mind when looking at survival rates. Only your oncologist can give you an accurate prognosis after careful consideration of the diagnostic results.
The US National Cancer Database indicates the following five-year survival rates for patients with Merkel carcinoma:
| Stage | 5-year survival rate |
|---|---|
| 1А | 80% |
| 1B | 60% |
| 2А | 60% |
| 2B | 50% |
| 3А | 45% |
| 3B | 25% |
| 4 | 20% |
For patients who have successfully treated Merkel cell carcinoma and achieved remission, doctors recommend staying under observation by a dermatologist. Following the examination schedule recommended by the doctor is the best way to detect a relapse quickly. One effective test in this regard is the AMERK biomarker blood test.
Clinics for the treatment of Merkel carcinoma
Summary
A Merkel cell carcinoma is an aggressive form of blood cancer that occurs most often in older people. The tumour takes the form of a pale or reddish nodule located on areas of the body that are exposed to the sun a lot.
Diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma, in addition to a biopsy of the tumour itself, includes a biopsy of the signal lymph node and a CT or PET scan of the body to rule out the presence of metastases.
Treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma depends on the stage of the disease and may include surgery, radiation therapy and immunotherapy, and in rare cases – chemotherapy. The prognosis of this disease depends on the stage, with an average five-year survival rate of 75-80% without metastases.
We recommend the following hospitals for treatment of the Merkel cell tumour abroad: Medicana Network and Liv Network (Turkey), Navarra University Hospital (Spain), Vienna Private Hospital (Austria), Cologne University Hospital (Germany), Ichilov Centre (Israel).
Make an appointment for treatment abroad
Mediglobus International Medical Tourism Platform is ready to assist you in all phases of organising your treatment abroad. Contact our medical coordinators for assistance by clicking on the button below and leaving your request.
Sources:
- 1. American Academy of Dermantology Association
- 2. NCNN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology for Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- 3. National Cancer Institute
:











