A pacemaker is a device that saves and extends life of thousands of patients around the world! But, to whom and in which cases is it installed, how to live after the operation, what are the dangers of installation? – issues that are important to clarify before the procedure. In an exclusive interview with MediGlobus about pacemakers, cardiologist Vadim Berezhnoi explains.
Read in an interview:
How the pacemaker is installed?
To whom doctors recommend the installation of an artificial pacemaker?
Are there any contraindications to the installation of a pacemaker?
Which examinations must be performed before installing the pacemaker?
What are the types of pacemakers?
How dangerous is the installation procedure of the device?
How does the patient’s lifestyle change after implantation?
VADIM, TELL ME HOW THE HEART WORKS, AND HOW WORKING WITH ARTIFICIAL PACEMAKER IS ESTABLISHED WITH PATIENT’S HEART?
The heart is one of the most important organ of the human body, which is constantly in work. By its structure, the heart is a muscle with cavities (atria and ventricles) and a valve apparatus, which alternately contracts and relaxes ensures the supply of nutrient-enriched and oxygenated blood to all cells of the body.
Despite the importance of this organ, few people know how the cardiac contractions occur and how they normally should be. To understand how this happens, it is important to understand the structure of this organ.
In addition to 4 chambers (two atriums and two ventricles), and a valvular apparatus, the heart has a complex electrophysiological system that generates electrical impulses that propagate throughout the myocardium through a conducting system.
The basis of the contraction of the heart muscle is an electrical impulse, formed in a special place – the sinus node, which is a bundle of special cells and located in the right atrium.
Formed impulse instantaneously spreads through the tissues of the right atrium causing it to contract, after which the impulse then travels through the conducting system to another important node – atrioventricular, whose main function is to slow the spread of the pulse. Slowing of the pulse in the AV node is physiologically designed to provide alternate atrial and ventricular contractions. The already delayed electrical impulse after the AV node extends to the ventricles, causing their contraction.
Such a process must be repeated certain number of times per minute, which is the heart rate (rhythm). Normally, the heart rate in an adult is 60 to 80 beats per minute. Slowing and increasing heart rate may occur due to physiological reasons, but there are also number of diseases that lead to severe rhythm disturbances, which necessitates rhythm correction, resorting the use of different medical tactics including the pacemaker installation.
HOW A PACEMAKER OR CARDIOSTIMULATOR IS INSTALLED?
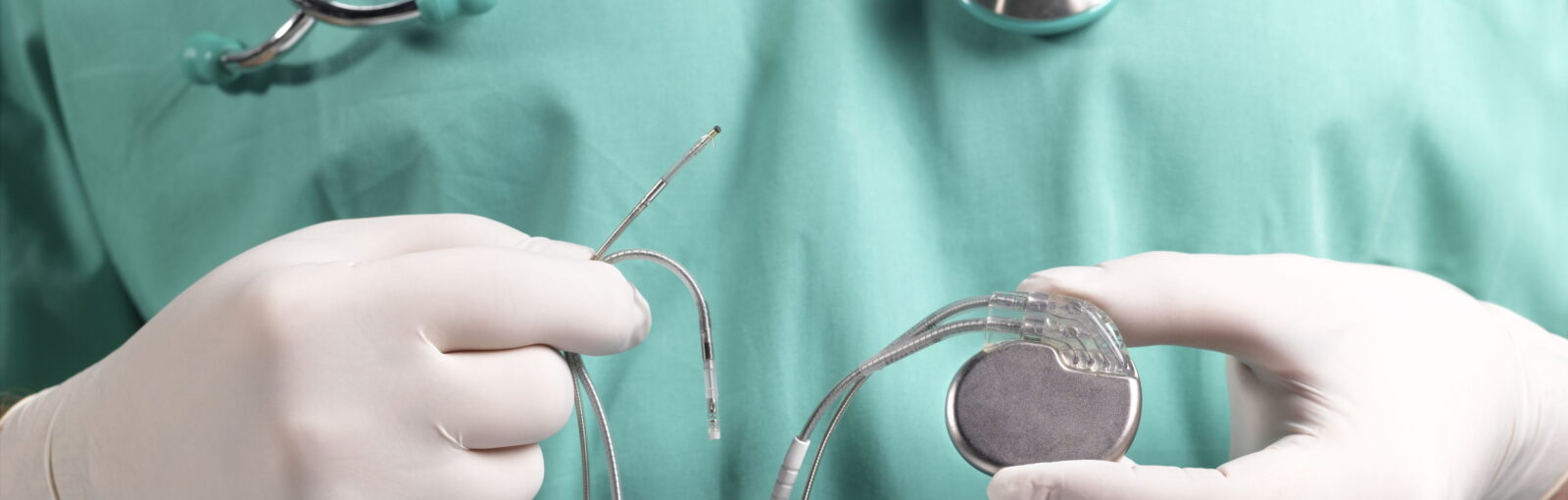
Pacemaker (artificial pacemaker, cardiostimulator) is a medical electronic device that affects the rhythm of the heart. The essence of the stimulator is to maintain or impose the normal heart rate of the patient and control the sequence of contractions in the chambers. The device consists of a generator implanted under the skin of the patient and electrodes that conduct an electrical impulse from the generator to the heart. Depending on the type of device, the number of electrodes can vary from one to three. In the generator case, in addition to the portable battery, there is a memory unit, an accelerometer, an antenna and a signal processor, as well as other sensors that record the patient’s condition depending on the model and purpose of the pacemaker. The generator body itself is always covered with a titanium layer, which reduces the risk of rejection to almost zero.
Note! Implantation and adjustment of a permanent pacemaker should be performed by a qualified arrhythmologist.
TO WHOM DOES THE DOCTORS RECOMMEND THE INSTALLATION OF THE ARTFICIAL PACEMAKER?
Implantation of a permanent pacemaker is indicated for patients with conduction disorders (intracardiac blockades), tachyarrhythmias (arrhythmias with high heart rate), bradyarrhythmias (arrhythmias with very low heart rate).
IMPLANTATION OF CARDIOSTIMULATOR IS CONDUCTED IN PATIENTS WITH:
- heart failure of severe degree;
- ventricular tachycardias;
- syndrome of weakness of the sinus node;
- atrioventricular blockade of 2-3 degrees;
- sinoatrial blockade;
- ventricular extrasystole after a heart attack;
- syndrome of the extended QT interval;
- blockade of the end of the bundle;
- severe recurrent attacks of supraventricular tachycardia;
- left ventricular failure.
In addition, clinical indications for implantation of pacemakers are: heart rate less than 40 per minute, intervals between contractions more than 3 seconds, syncope in tachyarrhythmia.
Is there any contraindication to this procedure?
Absolute contraindications to the pacemaker installation are not present, as there are no age limitations – the stimulant can be implanted regardless of the age of the patient.
Intervention to install a stimulant can be conditionally limited to the presence of acute inflammatory processes, as well as the patient’s mental pathologies.
WHICH INVESTIGATIONS DO I NEED TO PASS BEFORE INSTALLING THE PACEMAKER?
To select the type of cardiostimulator, you need to accurately determine the features of each patient, so your arrhythmologist will need the results:
- electrocardiograms (ECG);
- Ultrasound of the heart (echocardiography);
- Daily monitoring by Holter (daily ECG);
- ECG with stress tests (veloergometry or Treadmill test).
In some cases, coronary angiography and dopplerography of brachiocephalic vessels may be required.
What are electrocardio stimulator?
Cardiac Stimulators are divided into:
- Single-chamber (used to stimulate one ventricle or one atrium),
- Two-chamber (stimulate both a ventricle, and auricle),
- Three-chamber (stimulate both the ventricle and right atrium).
Separately, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators-devices not only control the rhythm of the patient’s heart beat, but also arrest life-threatening conditions, for example, ventricular fibrillation. Defibrillation occurs if the device detects a life-threatening rhythm, then an electrical impulse with a power of 10-35 J is generated, which restores the normal rhythm.
When choosing a stimulator, pay attention to the letters on the device model!
The current classification of pacemakers is developed in accordance with the recommendations of the North American Society for Electrophysiology and Pacing (NASPE), as well as the British Group for the Study of Electrophysiology and Stimulation (BREG). This is an alphabetic encoding using the Latin alphabet, where each letter means the type of stimulation, the place of fixation of the electrodes and the mode.
HOW DANGEROUS IS THE INSTALLATION PROCEDURE OF THE DEVICE?
Implantation of stimulators is considered a minor surgical intervention and is performed in a specially equipped operating room under X-ray control. The entire procedure is performed exclusively under local anesthesia (the skin area where the stimulator body is installed is anesthetized). The body of the stimulant is placed subcutaneously on the chest to the left, forming a bed of subcutaneous fat. After the vein is separated, through which the electrodes under the control of the X-ray are conducted into the chambers of the heart, where they are fixed (often the intervention is carried out through the lateral subcutaneous vein of the arm).
After the fixation of the electrodes is completed, the electrodes are connected to the device and the sensitivity of the stimulator is checked, after which the wound is sutured. The whole procedure takes no more than an hour. The risk of complications after the implantation procedure is no more than 5%.
HOW DOES THE PATIENT’S LIFESTYLE CHANGE AFTER IMPLANTATION PROCEDURE?
Patients who underwent stimulator implantation will have to visit their arrhythmologist once a week after the procedure to evaluate the device performance. For at least 3 months, any physical strain on the upper extremity belt is strictly contraindicated. Patients are forbidden sharp movements by hands and lifting weights.
In addition, for the normal operation of the device, each patient who has undergone the installation of an artificial cardiostimulator must adhere to certain rules:
- avoid exposure to electric current;
- the presence of a stimulant is an absolute contraindication to MRI;
- Contraindicated cosmetology procedures associated with electrical impact;
- It is necessary to avoid powerful magnetic fields and electromagnetic radiation zones;
- many methods of physiotherapy are contraindicated;
- It is forbidden to set the ultrasound probe on the body of the device;
- in no case should the apparatus be moved under the skin and avoid strikes in the area of the stimulant;
- Strictly forbidden monopolar coagulation during surgical interventions;
- you need to use a mobile phone on the opposite side of the stimulator.
Patients are often interested in how they go through the detectors at the airport or store. The control frames of detectors at airports and shops do not significantly affect the work of the stimulator, however, patients are not recommended for a long time in the area affected by these devices.