1. Proton therapy for glioma and glioblastoma |
2. Understanding the disease |
3. Proton therapy vs radiation therapy |
4. The procedure |
5. Efficacy and prognosis |
6. Clinics and costs |
Gliomas and glioblastomas are among the most common brain tumours, particularly in children. The danger of these diseases depends not only on the location of the tumour but also on its degree of malignancy. Proton therapy can in some cases be used to treat such patients.
Being a new method in cancer treatment, it is difficult for patients to find reliable information on the use of proton therapy to treat gliomas and glioblastomas. Therefore, we have decided to help out with this by analysing the most current research and consulting with experienced neuro-oncologists.
What is proton therapy and how can it help patients with glioblastoma/glioma?
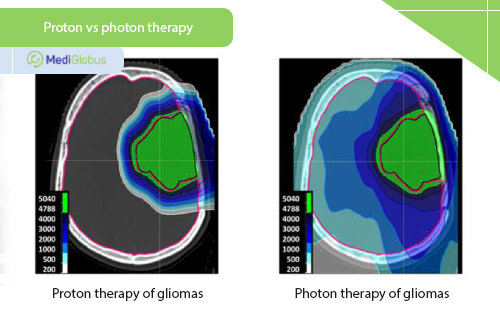
Proton therapy is a type of radiation therapy that uses small particles called protons instead of photons, as in ordinary radiation therapy. The difference between the two methods lies in the way energy is released during the movement of the beam. Whereas classic radiotherapy affects all the tissues through which the beam passes on its way to the tumour, proton therapy releases energy only on the target area. This has two main effects:
Doctors can use higher doses of radiation because they can worry less about the preservation of healthy tissue;
Because of the lower exposure of healthy tissue, patients deal with fewer side effects, which is particularly relevant for children.
Proton therapy allows doctors to destroy or shrink tumours without surgery. This method has proven most useful in cases where the cancer is located in hard-to-reach areas or near important CNS centres, making surgery more dangerous.
Due to the unique advantages of the method, paediatric cases are among the main indications for proton therapy for cancer. Children are more vulnerable than adults to some of the side effects of radiotherapy, such as secondary cancers and developmental delays. In adults, proton therapy for glioma can reduce the risk of cognitive impairment, lymphopenia and sensory deficits. This significantly improves the quality of life of cancer patients, which is a high priority in foreign medical centres.
In specialised cancer centres, an individual treatment plan is always drawn up for oncological patients. Doctors carry out a thorough diagnosis – both imaging and laboratory – to identify the “weak points” in the tumour and select the treatment approaches that will be most effective. A combination of several methods – surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy – shows the best results.
Therefore, proton therapy may not be indicated in all patients with glioma/glioblastoma. In general, it is most often used in cases where:
You need to have repeated radiation to treat a recurrence;
The tumour is near areas of the brain responsible for vision, hearing or other important functions;
The tumour is located in areas of the brain that cannot be operated on;
The shape and location of the tumour are not suitable for photon beam therapy.
To learn more about proton therapy abroad, please click on the button below and leave your contact details.
Features of glioblastoma and glioma treatment
To understand the particularities of proton therapy in the treatment of CNS tumours, it is necessary to understand the development and course of these diseases.
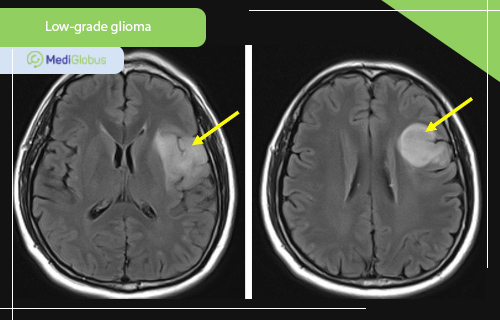
Glioma is among the most common types of brain cancer – it is responsible for about a third of all tumours. It affects the helper cells of the brain, the glia. There are low-grade and high-grade gliomas.
When treating patients with low-grade glioma, controlling the side effects of radiotherapy is a major challenge. Disruption of neurocognitive function is one of the most unpleasant of such complications. In this regard, proton therapy, with its reduced irradiation of healthy tissue, has great potential for use. It can deliver the necessary high doses of radiation while sparing healthy tissue.
Glioblastoma is a high-grade glioma. It affects astrocytes – the cells that support and serve neurons. Glioblastoma is difficult to treat. The danger of the disease lies in the high recurrence rate and the high aggressiveness of the disease.
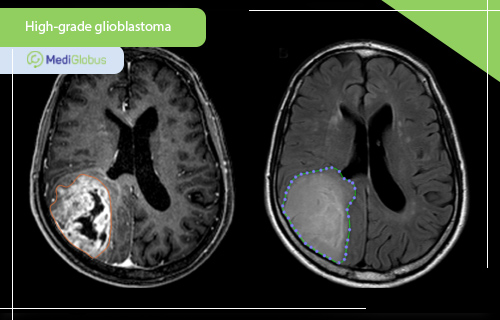
Glioblastoma tends to spread rapidly to neighbouring healthy tissue, so complete surgical removal of the tumour is problematic. Standard treatment protocols always supplement surgery with adjuvant radiotherapy to destroy the residual cancer cells as much as possible. In recent years, oncologists have started to pay more attention to the potential benefits of using proton therapy for this purpose.
Effective treatment for glioblastoma involves biomarker testing, which helps select drugs for specific genetic mutations present in the tumour cells. Studies show that chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy combined with targeted therapy can extend the life expectancy of cancer patients by several months. However, the difficulty in treating glioblastoma lies in the disruption of the blood-brain barrier, making drug therapy less effective than in other cancers.
Proton therapy is particularly relevant in the treatment of relapsed brain tumours. For patients who have previously received radiotherapy, repeated irradiation of healthy tissue with photons can be particularly dangerous. Proton therapy avoids this risk and allows glioblastoma or other types of glioma to be treated further. It is prescribed in cases where repeated surgical resection cannot be performed and the targeted therapy has not had the desired effect.
Which is better – proton therapy or radiotherapy?
There is no clear answer to this question. In some cases, proton therapy proves to be the best option for the treatment of glioblastomas and gliomas, and in others, there is no significant difference between the two therapies. Proton therapy centres have strict patient selection protocols to make sure that only those patients who can benefit the most from proton therapy will receive this type of treatment. Doctors will be able to make a recommendation after reviewing the patient’s diagnostic results.
Here are a few factors to keep in mind when comparing proton and radiation therapy:
It is important to start treatment of aggressive brain tumours quickly. In many cases, standard radiation therapy can be available much sooner than proton therapy. The number of cancer centres where the latter treatment option is available is limited, and patients may not be able to enrol for therapy without a waiting list. In such situations, most oncologists will advise not to delay treatment and to start irradiation with the available technology.
The effectiveness of the therapy differs from case to case. For some patients, proton therapy produces better results in irradiating the tumour, while for others, conventional (photon) radiation therapy achieves the same good results. In addition, there are some circumstances in which proton therapy is contraindicated. These include the rapid progression of the disease since postoperative imaging, the presence of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt, etc.
The ability of proton therapy to reduce the number and intensity of side effects depends on the radiation plan: the dose used, the location of the tumour, etc. In cases where oncologists use ultra-high doses of radiation, the patient will also have to deal with the side effects of proton therapy, the most dangerous of which is radiation necrosis. But it should be remembered that such high doses, which can play a critical role in the treatment of aggressive cancer, may not be possible with photon radiotherapy. At the same time, in individual patients, in whom the treatment field can completely cover a relatively small area of the tumour, the use of higher doses of radiation may ultimately be safe enough to be the best treatment option.
Proton therapy requires the use of very sophisticated equipment, unlike radiation therapy, making it a more expensive treatment option. The potential benefit of treating glioblastomas/gliomas with proton therapy must also be weighed against the budgetary burden. As a cheaper alternative, physicians may suggest radiation therapy options with low radiation exposure to healthy tissue – for example, FLASH therapy or IGRT.
How does proton therapy for brain gliomas work?
The preparatory phase for proton therapy of glioblastomas and other types of gliomas of the brain includes visualisation of the tumour, drawing up a treatment plan, preparing and positioning the device, and making a fixation mask.
1 | For the tumour to be irradiated accurately, doctors need fresh brain scans. To do this, a repeat MRI/CT/PET-CT is mandatory. The information obtained will then be downloaded into a computer, which will plot the radiation beam movement with millimetric accuracy. |
2 | Before treatment begins, a ‘simulation’ of the irradiation is carried out. This is necessary to set up the equipment correctly. The patient will be positioned in the same way as during the actual sessions, but the system itself will not be turned on. The doctors will map the brain, and clarify the location of the tumour and surrounding tissue. They will also make a custom-made head support mask to be worn at all subsequent sessions. |
3 | It may take several weeks to complete all the calculations and quality checks. The treatment itself for glioblastoma of the brain with proton therapy usually takes place every weekday for several weeks. Radiation exposure takes about 15 minutes and the entire visit to the treatment centre takes about an hour. |
Making an appointment for treatment
The international medical tourism platform MediGlobus is ready to provide you with free assistance in arranging your treatment abroad – collecting and translating documents, resolving organisational issues, getting a quick response from the clinic, finding an interpreter, etc. Leave your request online by clicking on the button below, and wait for a call from our coordinating doctors.
Effectiveness and prognosis of treatment
The long-term prognosis for low-grade gliomas with proton therapy shows a high survival rate combined with good quality of life. 84% of patients across the 5-year survival threshold, with stable cognitive, emotional and general functionality.
On average, the survival prognosis for patients with glioblastoma of the brain after high-dose proton therapy is 20-22 months, which is 5-11 months longer than with standard radiotherapy protocols. However, there is a risk of side effects with very high irradiation doses.
Studies investigating proton therapy for relapsed gliomas (including glioblastoma) have shown that the treatment is well tolerated by patients and has similar efficacy to photon therapy. A total of 95% of patients do not experience any severe side effects.
In addition, the risk of developing second cancer after proton therapy is five times lower than after conventional radiotherapy.
Studies carried out by foreign institutions show that proton therapy is most helpful for:
children with glioblastomas and other types of gliomas,
patients with good functional status,
patients with a favourable molecular profile,
patients with an increased risk of lymphopenia.
Where to go for proton therapy for cancer and how much does it cost?
There are only 89 medical centres around the world that offer proton therapy. This treatment will cost patients more than conventional radiation therapy. The price for proton therapy in foreign clinics starts at €60,000.
Among the clinics that accept glioblastoma patients for proton therapy, the international medical tourism platform MediGlobus can recommend the following:
Summary
Proton therapy is the optimal treatment option for some patients with gliosarcoma of the brain or other types of gliomas. It allows doctors to administer higher doses of radiation with fewer side effects. This treatment is best suited for children with brain tumours located in areas that are difficult to remove surgically (e.g. near the optic nerve), patients with good functional status, and for the treatment of recurrent gliomas.
Depending on the type of tumour and the dose of radiation used, the effectiveness of proton therapy can be on par with conventional radiotherapy or better. For some groups of patients, the use of proton therapy can improve treatment prognosis by 5-11 months.
For most patients with glioblastoma of the brain, however, photon radiation therapy will be a better treatment option for the tumour.
Among the foreign clinics offering proton therapy for their patients, we recommend the Quiron Salud Proton Therapy Center (Spain), the Proton Therapy Cancer Center in Prague (Czech Republic), the Carl Gustav Carus Clinic (Germany), and the Samsung Medical Center (South Korea).
Book an appointment for glioblastoma proton therapy
To book an appointment for glioblastoma proton therapy abroad, please click on the button below and leave your contact details. We will contact you within one hour and help with choosing a clinic and travel arrangements.
Sources:
- 1. Chinese Clinical Oncology: Proton radiotherapy for glioma and glioblastoma
- 2. Radiation: Proton Therapy and Gliomas: A Systematic Review
- 3. Radiotherapy and Oncology: Proton therapy for selected low grade glioma patients in the Netherlands









