According to the statistics published by the WHO, 10% of all cancer diagnoses are attributed to colon cancer. This disease is considered one of the most dangerous oncologies and has one of the highest mortality rates. The most unfavourable picture is observed in the Eastern European countries. Late diagnosis of the disease, older age of patients, non-compliance with check-up recommendations and carcinogenic lifestyle create additional issues in the treatment of colon cancer. This diagnosis requires a decisive and professional approach, and in this article, we will describe how patients are helped in leading foreign cancer centres.
What is colon cancer and what causes it?
Colon cancer is a malignant tumour found in the large intestine. The danger of this disease is that cancer cells grow uncontrollably and can spread throughout the body. Bowel cancer in the first stages, when it is easiest to cure, is often asymptomatic and a large number of patients do not receive timely treatment.
Often colon cancer develops from polyps – growths on the inner surface of the colon or rectum. However, it is important to note that polyp growth is normal, especially in older age, and most of them are benign. The World Health Organisation recommends that all people over the age of 45 should be examined by a proctologist, including colonoscopy, in order not to miss the moment when a bowel polyp becomes cancerous.
It is impossible to isolate a single cause of colon cancer. Often several factors play a role, for example:

Genetic predisposition;
Inflammatory bowel disease (e.g. Crohn’s disease);
Overweight and inactive lifestyle;
Unhealthy habits such as smoking, alcohol abuse and fatty foods.
People at risk are advised to monitor their health more closely and undergo more frequent check-ups.
Oncologists identify several types of tumours that can cause colon cancer. The type of the disease is found by biopsy and it affects the prognosis of the disease treatment and sometimes the approach to the patient’s treatment.
In 90% of cases, doctors diagnose adenocarcinoma of the colon. There are different subtypes of the tumour – mucinous, signet-like, medullary, micropapillary, dentate, cribriform comedo-type, adenosquamous, spindle cell and undifferentiated. They also differ among themselves in prognosis.
Carcinoid tumours, aka neuroendocrine tumours, form from hormone-producing cells in the intestine. They are usually slow-growing with a good prognosis for treatment.
Sarcomas of the large intestine are rare. This is an aggressive type of tumour, which is more difficult to treat and occurs in younger people.
Lymphomas can form in any part of the lymphatic system, including the large intestine. The disease predominantly affects men over 70 years of age. The survival rate depends on the histology and is about 67%.
Is colon cancer treatable?
Yes, colon cancer can be cured. The best prognosis is observed in patients whose tumour is localised in the intestinal wall and which can be completely removed by surgery. In more complex situations, doctors use adjuvant therapies, primarily chemotherapy and radiation therapy, as well as targeted therapy. The survival prognosis and treatment plan depend on the stage of the disease and the individual characteristics of the case. Leading foreign hospitals take these cancer patients very seriously and usually involve an oncology board – a consortium of leading hospital oncologists from different specialities – to find the most effective strategy.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT FOR BOWEL CANCER TREATMENT
We can help you select and book your treatment with an experienced overseas colon cancer treatment expert. Click the button below and leave your contact details so that our medical coordinator can contact you and help you organise your treatment abroad.
Diagnosis of colon cancer: symptoms, methods and markers
In the early stages, colon cancer is often asymptomatic, which is why the diagnosis is more often made in the later stages of the disease. In the presence of alarming symptoms, the doctor conducts an examination and prescribes a set of diagnostic procedures, which may include:
The main symptoms of colon cancer include stool irregularities, blood in the faeces, abdominal pain and swelling, chronic fatigue and sudden weight loss unrelated to external factors.
Stool analysis for hidden blood;
Blood tests for colon cancer oncomarkers: CEA and CA-19-0;
Bowel endoscopy;
X-ray with barium;
CT/NMR/PET-CT.
Current research shows that regular screening can reduce the incidence of colon cancer by 69% and mortality by 88%.
Source: Gastroenterology Scientific Medical Journal.
In advanced foreign clinics, a liquid biopsy may also be available. This diagnostic method is based on searching for fragments of tumour DNA in the patient’s blood, and its effectiveness has been particularly proven in screening for colon cancer. Liquid biopsy can also be useful when a conventional (needle) biopsy is problematic for one reason or another. Last but not least, this method can be used as a control of treatment efficacy and remission monitoring.
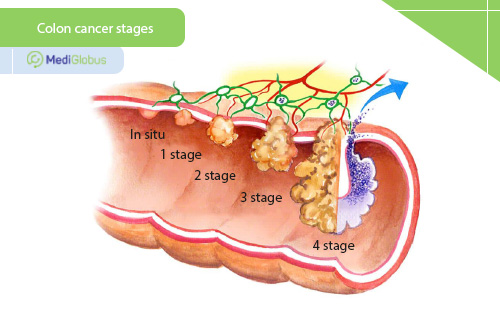
Treatment of colon cancer at stage 0
Stage 0, also called in situ, is the earliest stage of the disease. This is the ‘precancerous’ stage of tumour development when the growth is only in the upper layers of the inner bowel wall. It usually involves polyps with abnormal cellular structures. This stage of the disease has the best treatment prognosis and requires only surgery. Doctors can often remove polyps immediately during a diagnostic colonoscopy so that a separate procedure won’t be needed.
Treatment of colon cancer at stage 1
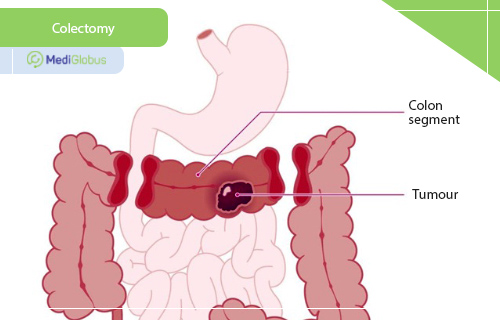
Stage 1 colon cancer is a tumour that is located in the upper layers of the inner wall of the bowel, penetrating the muscle. In stage 1, the main treatment is surgery. The doctor may perform a polypectomy (removal of the polyp), a local excision (removal of the polyp along with a small layer of tissue), or a colectomy (complete removal of a small part of the bowel, usually along with neighbouring lymph nodes). Chemotherapy or radiotherapy is not typically required for stage 1 colon cancer.
Treatment of colon cancer at stage 2
At stage 2, colon cancer has spread to the outer layers of the large intestine without affecting the lymph nodes. Depending on the depth of penetration, doctors divide this stage into sub-stages – 2A, 2B and 2C. Precise staging is important when planning treatment.
After running diagnostic procedures, an experienced oncologist will be able to suggest which treatment strategy will be most effective.
In some cases, surgery alone may be possible. Treatment protocols recommend colectomy for stage 2 large intestine cancer.
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy followed by surgery is a strategy that is used to shrink the tumour before intervention. This increases the likelihood of achieving “clear margins” (no cancer cells in the surrounding tissue) and subsequent remission. Various chemotherapy drug protocols are used to treat the disease at this stage.
Treatment of colon cancer at stage 3
Stage 3 colon cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes and may also spread to the peritoneum or neighbouring organs. This stage is also divided into substages 3A, 3B and 3C.
The surgical treatment for stage 3 colon cancer is colectomy. The risk of recurrence of the disease at this stage is quite high, so it is important to undergo chemotherapy to prevent it. For this purpose, various protocols can be used, the most common among which are FOLFOX and CapeOx.
For inoperable stage III colon cancer, the doctor can prepare the patient for surgery with chemoradiation. This is an aggressive combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy that is used to shrink the tumour to an acceptable size. Radiation therapy may also be used for stage III cancer after surgery if the tumour has managed to spread to a neighbouring organ or has positive resection margins.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT FOR BOWEL CANCER TREATMENT
The MediGlobus international platform works with +260 certified clinics worldwide. We will help you to find a clinic for qualified treatment of large intestine cancer of any stage and solve all issues with travel organisation. Consultations with our coordinating doctors are absolutely free of charge!
Treatment of stage 4 colon cancer
Stage 4 of colon cancer is also called metastatic. In this stage, the cancer process involves distant organs – most often the liver, lungs, and ovaries.
The process of treating stage 4 cancer is the most complex and multistage. Depending on the extent of the process, the doctor may suggest a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Targeted therapy is a special type of medication that can “recognise” cancer cells and destroy them in a targeted manner. Thanks to this, effective treatment can be achieved even in cases where chemo has not had the expected effect. For colon cancer treatment, the FDA has approved a large number of targeted drugs with different mechanisms of action, so there is a good chance of finding a drug that will work.
Immunotherapy – the use of drugs that help a person’s immune system to better recognise and destroy cancer cells. However, for these drugs to have the desired effect, they must be used against tumours with specific dMMR and MSI-H gene mutations.
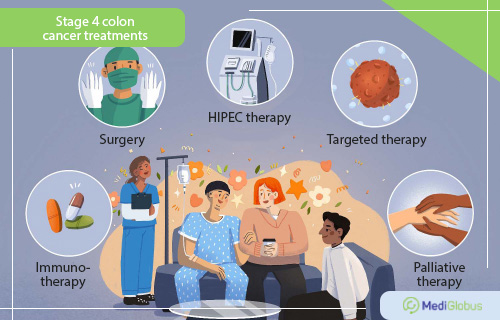
The prognosis of treatment for metastatic cancer is usually unfavourable and palliative treatment is often considered. Its aim is not to completely cure the disease but to control symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Among the procedures used to treat advanced stages of colon cancer, HIPEC therapy should be mentioned. It is a complicated procedure that is not available at every oncological centre. HIPEC is an open surgery that involves chemo being heated up to 42 degrees Celsius and poured inside the peritoneum. The high temperature and close contact with the cancerous tissues significantly increase the effectiveness of the treatment, achieving results not possible with classical chemotherapy.
Clinics for colon cancer treatment
Summary
Colon cancer has a good treatment prognosis at early stages but is rarely diagnosed in the asymptomatic period. The best way to detect the disease in time is to undergo all the age-recommended check-ups and examinations by a proctologist.
The main symptoms of colon cancer include stool irregularities, blood in the faeces, abdominal pain and swelling, chronic fatigue and sudden weight loss unrelated to external factors.
At stage 0, and sometimes at stage 1, the disease can be completely removed by polypectomy. From stage 2 onwards, colectomy becomes the leading surgical treatment. It may also be joined by chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In advanced stages of colon cancer, immunotherapy, targeted therapy and HIPEC therapy may be used.
For colon cancer treatment abroad, the international platform MediGlobus recommends going to Liv and Koç clinics (Turkey), Teknon Hospital (Spain), Cologne University Hospital (Germany), Vienna Private Clinic (Austria) and Fuda Clinic (China).
APPOINTMENT FOR CANCER TREATMENT
To enrol for cancer treatment abroad, click on the button below and fill in the form. Our coordinating doctors will call you back to answer all your questions and help you with organisational problems.
Sources:
- 1. American Cancer Society
- 2. World Health Organization
- 3. Colorectal Cancer Alliance
- 4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- 5. Gastrointestinal Cancers
- 6. World Cancer Research Fund International
- 8. Clinics in Colon and Rectal Surgery
- 9. Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- 10. Gastroenterology
- 11. Cancers (Basel)












