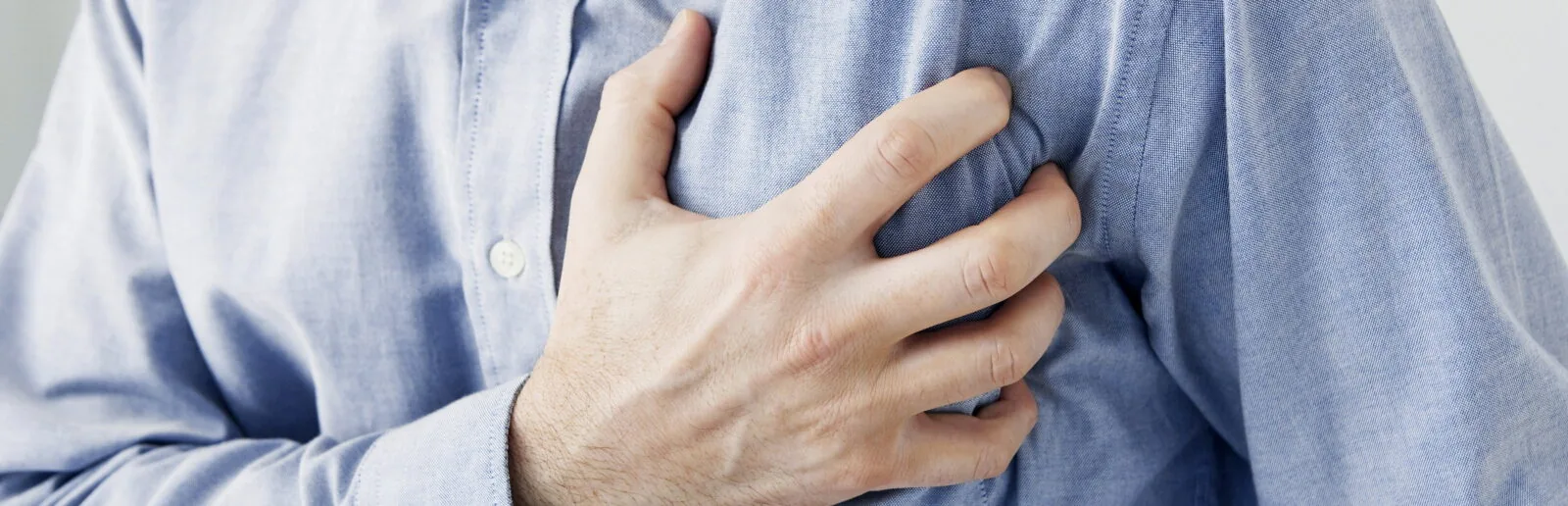
According to data published by the World Health Organization, 32.4 million new cases of acute myocardial infarction are registered worldwide every year. Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in the world. According to official statistics, only for 2012 cardiovascular diseases caused death of 17.4 million people, 7.4 million of whom died due to acute myocardial infarction.
Myocardial infarction or heart attack is an acute condition characterized by a substantial or complete cessation of the blood supply to the specific area of the heart muscle with subsequent necrosis. Infarction develops as a consequence of coronary heart disease. This condition is dangerous and can lead to death in case of untimely diagnosis and medical care.
READ IN THE ARTICLE:
Who is at risk of heart attack?
Prevention of myocardial infarction
Main Factors of Infarction
The main factor in the development of myocardial infarction is the overlap (obturation) of the lumen of the coronary vessel. Obstruction of the lumen can develop due to
- atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries (overlapping with a plaque),
- complications of surgical interventions (eg restenosis after angioplasty),
- embolization of the coronary arteries (fat embolism, thrombosis),
- sudden spasm of coronary vessels.
Who is at risk of heart attack?
There are number of circumstances, the so-called risk factors that predispose to the development of a heart attack:
- Sex – men are much more likely to suffer a heart attack than women.
- Age – the older the person, the higher the risk.
- Smoking (including passive) several times increases not only the risk of heart attack, but also increases the death rate of patients who have had an infarction in half.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages (alcohol and its decay products have a toxic effect on heart tissue).
- The state of constant emotional stress (frequent stress).
- Hypodinamy (low physical activity and passive lifestyle increase the risk of heart attack 5 times).
- Excess body weight, obesity (leads to disruption of metabolism and imbalance of lipid fractions in the blood, which in turn is the cause of the development of fat deposits in the walls of the arteries).
- Diabetes.
- Weighed down by heredity.
- Arterial hypertension.
The risk group of recurrent myocardial infarction includes patients who had previously had a heart attack and patients with ischemic heart disease who do not take adequate medication.
Prevention of myocardial infarction
Prevention of acute myocardial infarction can be divided into primary and secondary.
For the primary prevention of a heart attack, it is enough to change the way of life, thereby reducing the risks.
- It is necessary to lead an active lifestyle, giving the body proper physical activity (each day an adult is supposed to walk at least 5 km);
- To adjust the diet, reducing the consumption of fatty, roasted, smoked and pickled food. Increase the number of vegetables and fruits, foods rich in fiber and polyunsaturated OMEGA-3 fatty acids;
- Limit the use of salt (no more than 3 grams per day);
- Avoid stress or learn to cope with stressful situations.
Secondary prophylaxis of a heart attack may include medical correction. As a rule, this is relevant for patients who were diagnosed with cardiac pathology, a previous heart attack and the presence of complicating diseases such as diabetes, obesity and so on. It is necessary:
- To control the level of pressure and keep it within the limits of acceptable values (timely correction of preparations from pressure and their dosage). Thus, a group of ACE inhibitors can be used to prevent infarction in individuals with a reduced ejection fraction;
- Antiplatelet therapy significantly reduces the risk of recurrent myocardial infarction. The most commonly used drugs are acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) or clopidogrel;
- The use of beta-blockers in people who have had a heart attack with a reduced ejection fraction reduces the mortality rate;
- Statin therapy slows the progression of atherosclerosis;
- The use of multivitamins in combination with polyunsaturated OMEGA-3 fatty acids provides a good overall supporting effect.
General recommendations
Adapting to an active lifestyle and healthy diet, controlling your weight and blood sugar level, cholesterol and triglycerides, avoiding certain bad habits can significantly reduce the risk of heart attack and cardiovascular disease in general.
But most importantly – do not self-medicate! Cardiac diseases can have different causes of occurrence, it is necessary to undergo a survey. Be sure to consult a specialist for any symptoms of heart disease.
Take care of yourself!

Dr. Vadim Berezhnoy