Read in the article:
Indications and contraindications
Rehabilitation in the postoperative period
Consequences and complications after procedure
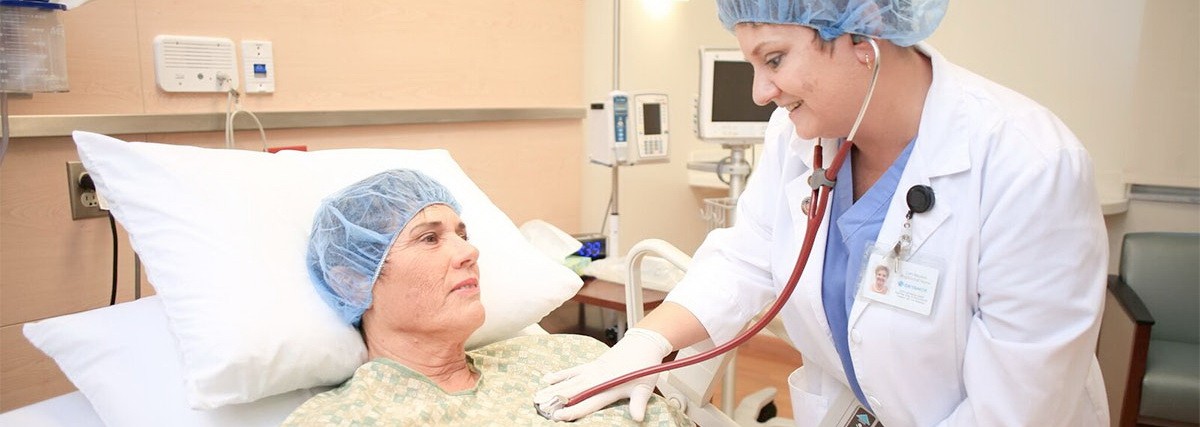
Many patients who suffer from cardiac diseases for a long time are prescribed a procedure such as bypass surgery. Mediglobus felt a need to explain the features of this procedure, its indications and contraindications, etc. We asked the doctor-cardiologist Vadim Berezhnoi to answer all these questions.
VADIM, TELL US ABOUT THIS PROCEDURE?
Aortocoronary shunting (CABG) is one of the most common surgical procedures in modern cardiac surgery use to treat patients suffering from critical narrowing of the coronary artery lumen.
The aim of this procedure is to restore normal blood flow by imposing a bypass (vascular shunt) between the affected coronary artery and the aorta. This need arises with a critical narrowing or complete blockage of the coronary artery lumen by an atherosclerotic plaque in ischemic heart disease. A similar condition of the coronary arteries leads to prolonged ischemia (insufficient blood supply) or the complete cessation of the blood supply of a specific area of the heart muscle (myocardium) with a high risk of developing an acute myocardial infarction and the patient’s death.
As a rule, the narrowing of the lumen of the arteries is clinically manifested by severe pain behind the breastbone even with the smallest physical effort.
TO WHOM AORTO-CORONARY SHUNTING IS INDICATED AND CONTRAINDICATED?
MAIN INDICATIONS FOR CABG:
- Inefficiency of endovascular methods of IHD treatment (balloon angioplasty and stenting);
- Narrowing of the left coronary artery lumen by more than 50%;
- Multiple narrowing of the coronary arteries;
- A critical narrowing of the anterior interventricular artery at the site of the latter from the central artery;
- Stable angina 3-4 functional class;
- Unstable angina not amenable to drug correction.
AMONG CONTRA-INDICATIONS TO CARRYING OUT THE CABG ARE:
- Severe congestive heart failure;
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Extensive stroke;
- Terminal stage of kidney and liver diseases;
- Severe lung disease;
- Previously suffered extensive heart attack with severe contractility of the myocardium;
- Multiple narrowing of the coronal vessel lumens in their terminal regions;
- Old age is a relative contraindication, each such case is considered strictly individual.
CABG is a rather complicated procedure and requires the doctor to have the appropriate skills and professionalism.
YOU MENTIONED THAT THE PROCEDURE IS COMPLEX, DISCUSS WHY AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
FOR THE CREATION OF THE BY-CARE SHUNT, WE USE THE PATIENT’S OWN TISSUES:
- Subcutaneous veins of the lower limb (autovenous coronary artery bypass graft)
- Radial artery from the forearm (autoarterial coronary artery bypass)
- Internal thoracic artery (mammarocoronary bypass)
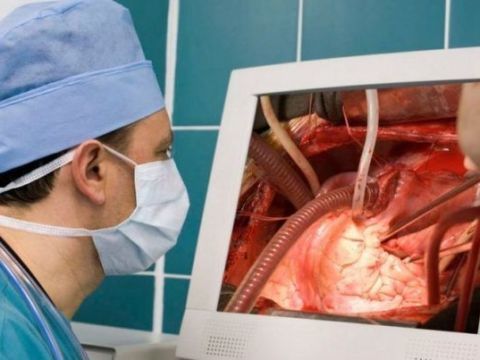
The sampling of the material for creating the shunt is performed by open or endoscopic methods. More often vascular discharge is performed endoscopically with the aim of minimizing trauma, accelerating wound healing and a better aesthetic effect. Endoscopic sampling of the material along with standard surgical techniques has advantages for patients with impaired peripheral blood supply, diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, aged patients and so on.
As a rule, the duration of surgical intervention of CABG is 3-4 hours on average. The operation involves a team consisting of cardiac surgeons, perfusiologists and anesthesiologists. Coronary artery bypass grafting can be performed both on the working heart and with cardiac arrest and patient connected to the artificial circulation device (AIC).
Important! The type of operation is chosen exclusively by a cardiac surgeon depending on the individual characteristics of each patient, the severity of the condition and the need for an additional operation (e.g reconstruction or replacement of valves). The number of shunts is determined depending on the severity of the disease. Up to 3 shunts can be generated for one intervention.
A timely operation can prevent not only irreversible changes in the myocardium, but also significantly reduce the risk of developing a heart attack, thereby saving a patient’s life.
VADIM, WHAT IS THE PREPARATION FOR THE PROCEDURE OF SHUNTING?
THE MAIN STAGE OF PREPARATION IS THE INVESTIGATION OF THE PATIENT THAT INCLUDES:
- General and detailed biochemical analysis of blood,
- ECG at rest,
- ECG with loading tests,
- Holter monitoring,
- Ultrasound of the heart,
- Diagnostic coronary angiography.
As a rule, it takes up to 3 days for additional examination, depending on the doctor’s appointments. In the evening before the operation, the patient should take a light dinner. Morning on the day of surgery, the patient should not eat, an anesthesiologist is inspected and the medical staff accompanies the patient to the operating room. Immediately after the operation, the patient is transferred for several days to the intensive care unit, after which he is hospitalized in the general ward regime. The sutures are removed in the interval from 9 to 14 days after the operation.
IS THERE ANY COMPLICATION AFTER OPERATION, HOW THE PATIENT LIVE AFTER THE PROCEDURE?
The percentage of early complications is about 4-6%. To early complications after the operation include thrombosis from shunt, stroke, heart attack, suppuration of the wound. The average duration of shunt operation is more than 10 years.
According to statistical data and patient survey data, about 70% of patients seem to have complete disappearance of symptoms after shunting and about 20% feel improvement in condition. Subject to strict adherence to doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations, more than 85% of patients manage to avoid the development of atherosclerosis of the shunt.
PATIENTS MAY BE RECOMMENDED SHUNTING AND STENTING, WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PROCEDURES?
It can not be said that CABG has advantages over coronary stenting. Each procedure, whether balloon angioplasty, stenting or shunting, has its own specific indications and the degree of effectiveness at one stage or another.
Stenting is a minimally invasive procedure with access through the vessel (endovascular) and is ideal for patients with mild to moderate arterial narrowing.
Shunting is a full-fledged surgical procedure that requires a longer recovery period and is applicable mainly for severe and critical narrowing of the coronary vessels.