According to WHO one of the most common causes of death in the world, is cardiovascular disease. In particular, coronary heart disease accounts for more than 40% of all cases.What you need to know about stenting before going through the procedure, explained by cardiologist Vadim Berezhnoy.
READ IN THE INTERVIEW
How is angioplasty stenting performed?
How to choose a stent for the patient?
To whom stenting procedure is recommended?
Contraindications to the procedure of stenting
How dangerous and traumatic is the procedure?
Patient’s life after angioplasty stenting procedure
Is there an expiration date for the stent?
VADIM, EXPLAIN THE CAUSES OF ISCHEMIC DISEASES
“Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a fairly common disease that arises from a decrease in the lumen of the coronary arteries due to a particular disease, which leads to reduction or cessation of arterial blood flow to the heart muscle. The main cause of the development of ischemic heart disease is atherosclerosis (the lumen of the arteries is narrowed by the gradual deposition of cholesterol in the walls of the artery).
One of the methods of surgical treatment of ischemic heart disease along with shunting is the stenting of the coronary arteries. This method is considered an alternative choice with respect to bypass surgery. ”
And how is the procedure of stenting carried out?
“Stenting of the coronary arteries is a minimally invasive intervention used to restore the lumen of the cardiac arteries and restore normal blood flow to them.
The stent is a thin lattice metal tube that straightens directly the affected area inside the vessel, thereby forming a stable framework. The function of the stent is to maintain the walls of the artery in a stable position. ”
How does the patient choose a stent?
“Today two main types of stents are actively used: uncoated (holometallic) and coated (with the application of a drug on the metal surface of the stent).
Covered stents differ from holometallic by the presence on their surface of a polymer layer and a layer of medicinal substances. The medicines applied to the stent surface reduce the risk of stent overgrowing and thrombus formation. The polymer layer reduces the rate of leaching of drugs, thus contributing to a longer lasting effect.
Important fact: The risk of restenosis in covered stents is no more than 3%, in holometallic 30-40%.
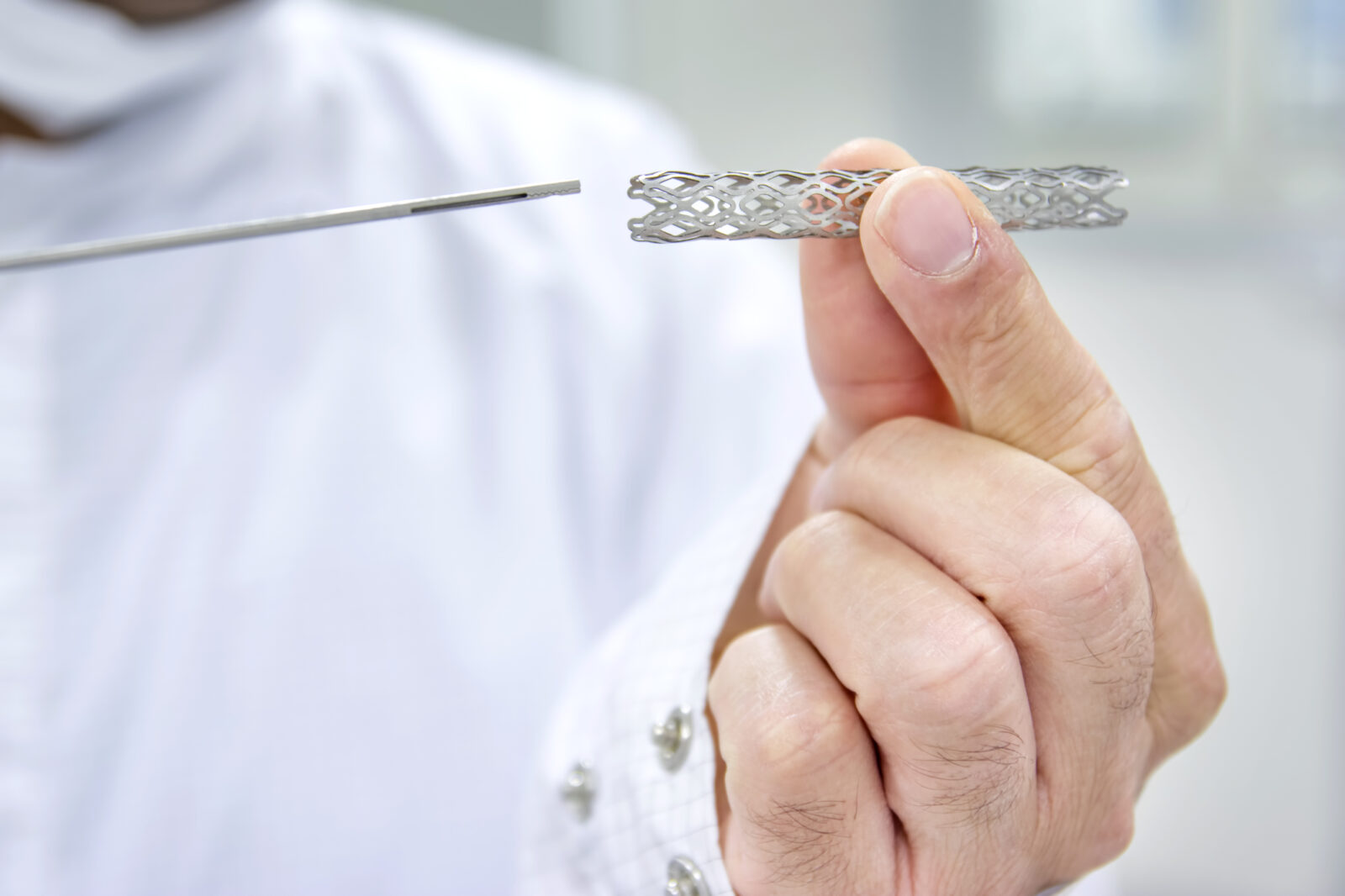

Most often in practice, coated stents are used, their service life is much longer than uncovered. Uncovered stents, are used in modern medicine but only in certain cases, since the risk of thrombosis and the development of complications is much higher than that of the coated ones.
Stents are developed from a resorbable material (biodegradable). Such stents dissolve at least two years after installation. The use of such stents has a number of advantages (reducing the risk of complications, restoring the pulse wave along the vascular wall after resorption), but the possibility of using this type of stent should be evaluated by the doctor in each individual case.
The stents may also differ in the alloy from which they are produced and the type of the framework cells. The choice of the type of stent and their number is generally determined solely by the individual characteristics of the organism of each patient. Stenting can be performed urgently during diagnostic coronary angiography, which makes this a method of choice in the case of acute myocardial infarction. ”
TO WHOM STENTING PROCEDURE IS RECOMMENDED?
BASIC INDICATIONS FOR CONDUCTING STENTING ARE:
- acute myocardial infarction (in the first hours after the infarction);
- angina at rest;
- 3rd-4th functional class of angina pectoris;
- latent ischemia of the myocardium (detected by accident according to the studies results);
- rheostatosis (repeated stenosis) at the site of a balloon plastic or stenting performed earlier;
- acute thrombosis of a previously established stent;
- with the resumption of angina after shunting.
ARE THERE CONTRAINDICATION TO THE PROCEDURE?
“There are no absolute contraindications for this method. An exception can be unless the patient refuses treatment.
RELATIVE CONTRAINDICATIONS CAN BE :
- severe pulmonary (respiratory) insufficiency;
- severe renal failure;
- coagulopathy (bleeding disorders);
- individual intolerance to iodine preparations (iodine is part of the radiopaque substance used during the procedure.In the case of allergic reactions to iodine, specific therapy is used before treatment for preventing complications);
- extensive changes in the artery, making stenting impossible.
DO WE NEED ANY SPECIAL EXAMINATION BEFORE STENTING?
BEFORE THE PLANNING PROCEDURE OF STENTING, A LINE OF LABORATORY AND INSTRUMENTAL TESTS ARE PROVIDED:
- general and biochemical analysis of blood (including coagulogram – indicators of blood coagulability);
- ECG;
- Echocardiography (ultrasound examination of the heart);
- Coronary angiography (x-ray endovascular study of the patency of the heart arteries is the gold standard for the diagnosis of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease).
- Urgently (for example, with acute myocardial infarction), stenting can be performed immediately in the process of coronary angiography (angiography of the heart vessels), in such case the procedure becomes not diagnostic, but – therapeutic.
HOW DANGEROUS AND TRAUMATIC IS THE PROCEDURE?
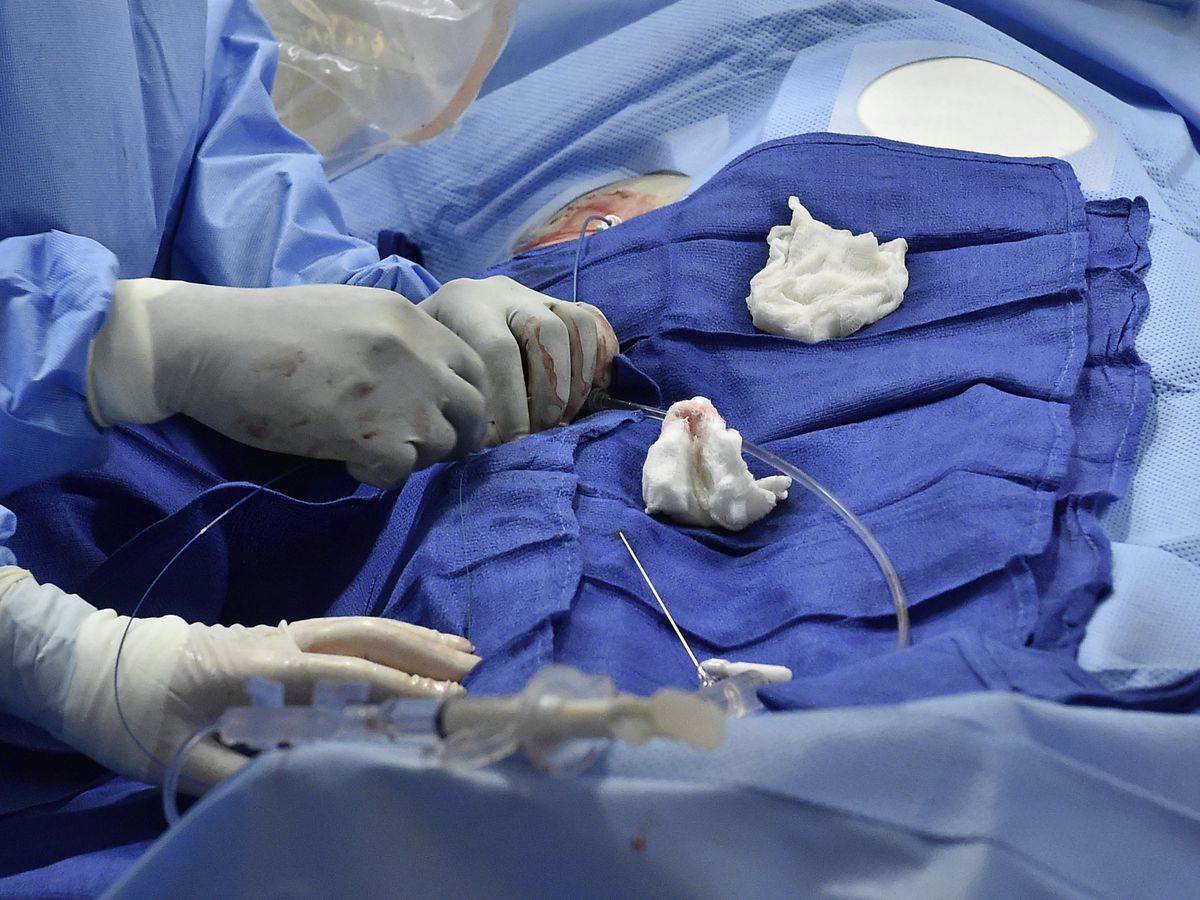
“The procedure is virtually bloodless, does not require a long recovery period and prolonged hospitalization. Through the puncture of the artery (femoral or radial on the wrist), a catheter is inserted into the circulatory system of the patient, at the end of which the balloon is located. The stent is fixed on the balloon before. Surgeon gently moves a catheter with a balloon and a fixed stent the patient’s vascular system directly to the site of stenosis. At the necessary place the balloon swells, which leads to the expansion of the stent. The inflated balloon widens the artery lumen and fixes the stent on the vessel wall.
The operation is carried out under the control of a special X-ray installation in real time, the surgeon monitors the process by watching the video monitor.
Depending on the complexity of the situation, the procedure may require 1 or 2 stents. To improve visualization of artery walls during the entire procedure, a special radiopaque substance based on iodine is administered to the patient in portions.
After placing the stent at the site of stenosis of the artery, the catheter is removed in the same way and a tight bandage is applied to the surgical site.
DOES THE PATIENT’S LIFE CHANGE AFTER STENTING?
Life after stenting involves taking medications for the underlying disease that led to stenosis of the coronary arteries (drugs that lower cholesterol, drugs to control blood pressure and heart rate, etc.).
Patients may be seen taking medications that dilute the blood (clopidogrel or aspirin), which are prescribed by the doctor on individual basis.
Moderate physical activity, regular walking on fresh air, food restrictions with high cholesterol or simple carbohydrates – these are the requirements of prevention, which are necessary after the procedure of stenting. In addition, patients are recommended a clear separation of the work and rest regimes.
IS THERE ANY VALIDITY PERIOD FOR STENT?
“As a rule, stents are designed for a long time, but the duration of the stent can be significantly reduced due to individual characteristics of human life, the presence of bad habits and non-compliance with the recommendations of the treating doctor. Replacement should be overgrown stents, which led to restenosis. Also, patients who had previously been placed with a bio-dissolving stent, who due to improper operation had resolved faster than standard time, are subject to re-stenting.
With all the doctor’s prescriptions, the use of preventive measures, and also with the help of a competently matched and established stent, the patient can live a long and comfortable life. ”





